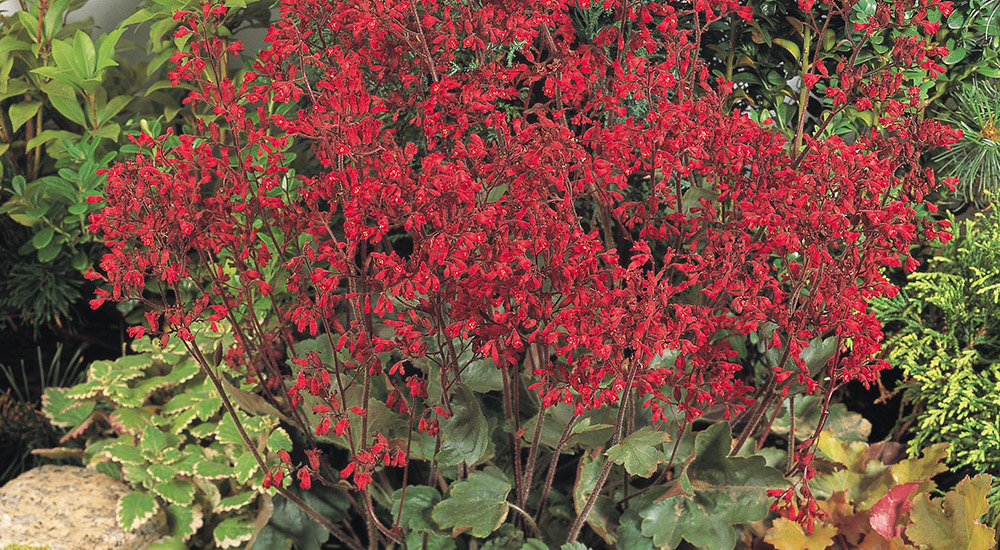
Ruby Bells
- Decorative evergreen leaves
- Well-branched plant habit
- Attractive deep red flowers
- Perfect for bedding and rock gardens
- Optimal storage: up to 6 months at 5 °C / 41 °F
- Crop Time
- Spring: 24 - 25 weeks
- Height ∅
- 16 ″ / 40 cm
- Exposure
- Partial shade - Shade
- Seed Form
- Raw Seed, BeGreen ApeX Pelleted
- Heat Zone
- 8-2
- Hardiness Zone
- 3a-8b
- Product Use
- Bedding, Cutflower, Landscape
Technical guide
Usage
Wintergreen plants for border and rock garden, pot and container plants, plants attractive for bees and butterflies, cut flower production, ornamental leaf production
Sow time
December-April for green pots, June-August for flowering in pots the following year
Sowing method
3-5 seeds per plug
Germination
10-20 days at temperatures of 68-72 °F (20-22 °C), keep relative humidity levels near 95 %. Stage II & Stage III maintain temperatures between 65-70 °F (18-21°C). Stage II relative humidity should remain near 95 % and gradually lowered during Stage III. Begin feeding at 50-75 ppm nitrogen in a well balanced mix at Stage III. Stage IV temperatures can be lowered gradually to tone plants. Large plugs can be vernalized.
Growing on
Transplant plugs after 9 weeks. Grow on at 55-60 °F (13-15 °C). Vernalization is required for flower initiation. After vernalization, begin forcing plants at 60-65 °F (15-18 °C) under long days for 7-8 weeks.
Media
Use a well-drained, growing perennial substrate with 0-15 % clay, 0-15 % parts (e.g. bark, wood fibres), 1-1,5 kg/m³ complete balanced fertilizer, 2-3 kg/m³ slow release fertilizer (3-9 months), iron-chelate, micronutrients, pH: 6.0-6.5. Field: sandy humus soils with good drainage. Standard fertilization: 50-80 g/m² of a slow release fertilizer.
Temperature
Grow at 15-18 °C or outdoors. In winter indoors frost free at 3-5 °C or outdoors. Outdoor fleece cover needed. In spring the plants start to grow for 9-12 weeks at 10-18 °C. Warm temperatures will decrease the cultivation time. A chilling period (vernalization) is required for flower initiation.
Fertilization
High fertilization levels are required. Fertilize the crop weekly with 130-150 ppm nitrogen (at 3 kg/m³ slow release fertilizer in substrate), using alternating a potassium balanced fertilizer (N: K₂O-ratio: 1:1,5) and a calcium nitrate fertilizer. Avoid high ammonium and high nitrogen levels. Don’t fertilize after mid September. In spring fertilize 130-150 ppm nitrogen of a complete balanced fertilizer (N: K₂O-ratio: 1:1,5). Prevent magnesium deficiency by applying magnesium sulphate (0,05 %) 1-2 times and in case of iron deficiency (above pH 6.0) apply iron-chelate for 1-2 times. Very high nitrogen levels can be cause that the leaves fall apart and that the application of growth regulators will become necessary. Field: If necessary according to analysis, improve the soil with 50-80 g/m² of a slow release fertilizer, applied in several portions.
Stage I Starts with the radicle breaking through the testa. The roots are touching the medium. Ends with fully developed cotyledons.
Stage II Starts from fully developed cotyledons. Ends with the fully developed true leaf or true leaf pair.
Stage III Starts from the fully developed true leaf or true leaf pair and ends with 80% of the young plants being marketable.
Stage IV All young plants are ready for sale and in the process of being hardened off. This stage lasts about 7 days.
The cultural recommendations are based on results from trials conducted under Central European conditions. Different conditions in other parts of the world may lead to deviations in results achieved.